Article 1 - The ASEAN Power Grid Opportunity
Exploring the Potential of Cross-Border Energy Trading and the ASEAN Power Grid
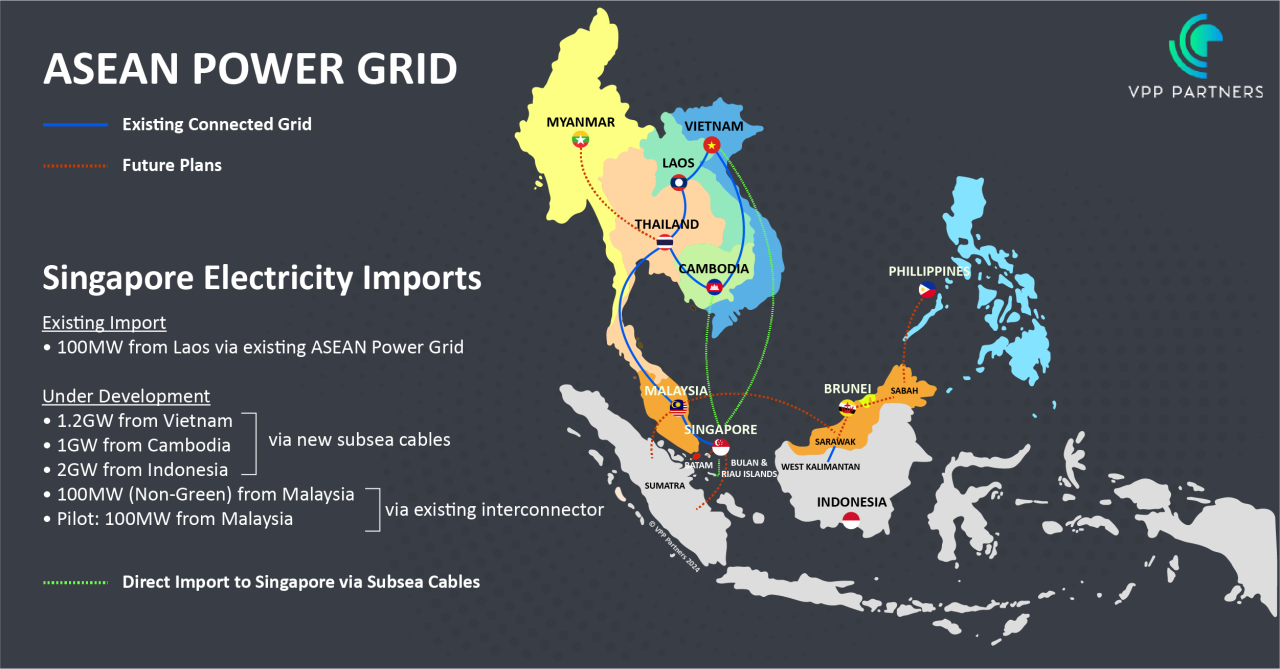
In the quest for sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions, the concept of an interconnected ASEAN Power Grid has emerged as a promising strategy. This ambitious initiative aims to link the energy networks of various ASEAN countries, facilitating cross-border energy trading and unlocking a multitude of benefits for the region.
Strategic Importance of an ASEAN Power Grid
The strategic importance of an ASEAN Power Grid cannot be overstated. By interconnecting the energy infrastructures of nations across Southeast Asia, this grid would enable seamless cross-border energy flows. Such connectivity could bolster energy security, diversify energy sources, and enhance resilience against supply disruptions.
Recently, Malaysia made headlines with its energy sector tender, which, while initially appearing unattractive to investors restricted to only retailers and generators, signifies a critical test bed for market entry. This initiative highlights the early stages of cross-border energy trade developments, underscoring the potential for growth and innovation in the region.
Cost Reduction for Net Zero Emissions
Studies suggest that an ASEAN Power Grid could play a pivotal role in reducing costs associated with achieving net-zero emissions. By optimising the utilisation of renewable resources across different time zones and geographic regions, surplus energy could be efficiently distributed, reducing the need for costly backup infrastructure and storage technologies.
Promoting Sustainable Energy Development
In Southeast Asia, where energy demand is rapidly growing, sustainable energy development is imperative. The ASEAN Power Grid could accelerate the adoption of renewable energy sources by creating a broader market for clean power. This, in turn, could drive investment in renewable infrastructure and technologies, fostering economic growth while mitigating environmental impacts.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
The economic advantages of a robust cross-border energy trading system are substantial. Enhanced market integration would promote competition, leading to lower energy prices and improved efficiency. Moreover, the environmental benefits of reduced carbon emissions and optimised resource utilisation align with global efforts to combat climate change.
VPP Partners believes that the vision of an interconnected ASEAN Power Grid holds tremendous promise for the region. While challenges persist, recent initiatives like the Malaysian tender serve as crucial stepping stones toward realizing this vision. By leveraging cross-border energy trading, Southeast Asia can chart a course toward sustainable energy development, economic prosperity, and environmental stewardship.